
% ddt -start -break-at timestep /usr/bin/python laplace.py
SIMPLY FORTRAN DEBUGGING CODE
Let's make it breakpoint at the function timestep - to stop the process as soon as it reaches the code we are interested in. Let's take inspiration from this Laplace example from the SciPy Performance Python pages - which computes several iterations of Laplace transform on a matrix, using various implementations including native code.Īnd now we execute inside DDT. As soon as your native code executes, the debugger will be debugging it. For Python scripts that call F90 or C++ directly, say, that code is executed within the same Unix process as the Python itself – so we start the debugger by having it debug that process.
Let's see how we'll tackle that (C++ users can use exactly the same method).Īrm DDT is a native code debugger – which means it can’t debug the python script – but it can debug any native code that is used by a process. So, you think you have a bug in some Fortran/F90 called from inside Python. Debugging Fortran and F90 in a mixed Python Code It's worth noting too that the techiques here apply equally easily for the mpi4py package for almost all MPI implementations. You can still use your Allinea tools debug your Fortran – even if it’s been invoked from Python – and then profile the whole application so that we can improve its performance.
SIMPLY FORTRAN DEBUGGING HOW TO
We’re regularly asked how to debug or profile codes invoked or steered by Python – so today we’re going to show you how it’s done. Indeed, NumPy itself brings in routines from the BLAS libraries – providing hyper-efficient numerical matrix routines into the world of Python. With f2py, any Fortran code can be used within a Python script. One of the most popular methods for Fortran developers is to use the f2py utility – part of the NumPy package.
However, using native code such as code written in C, C++, F90 is easy from within Python scripts – and that’s why Python and C++ or Fortran are a popular combination. Its interpreter simply can’t apply the advanced optimizations to your loops and floating point operations that a C++ or Fortran compiler can. It is easy to code and powerful - but numerical computation is not a strength that Python has. It sets a breakpoint at a specified line.Įxecutes only the next line of source code, without stepping into any function call.Python is pretty commonplace in scientific computing these days. It stops execution when a procedure proc is entered Sets a breakpoint when the value of variable var changes. The following table provides some commands in dbx − Command There is another debugger, the dbx debugger, for Linux.
SIMPLY FORTRAN DEBUGGING WINDOWS
For X windows system, gdb comes with a graphical interface and the program is named xxgdb.įollowing table provides some commands in gdb − CommandĮxecutes only the next line of source code, without stepping into any function callĮxecute the next line of source code by stepping into a function in case of a function call. The gdb debugger, the GNU debugger comes with Linux operating system. Watch points are the points where the values of some variables are needed to be checked, particularly after a read or write operation.

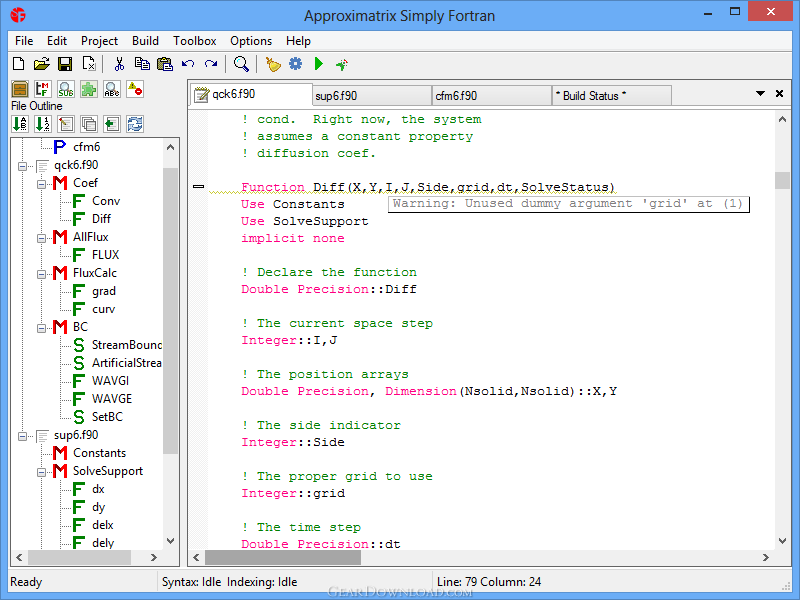
Program executions after the variables are checked at a breakpoint.ĭebugger programs also check the source code line by line. Debuggers debug a program by −īreakpoints specify where the program should stop, specifically after a critical line of code. It loads the source code and you are supposed to run the program within the debugger. A debugger tool is used to search for errors in the programs.Ī debugger program steps through the code and allows you to examine the values in the variables and other data objects during execution of the program.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
